Nutrients: The Essential Nutrition Used in Powerful Hydroponic Systems
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Hydroponic farming has revolutionized agriculture by allowing plants to grow without soil. Among its many variations, aeroponic farming stands out for its efficiency and resource conservation. However, the success of any hydroponic system depends on the right balance of nutrients. Understanding these essential nutrients and their role in plant growth can help farmers maximize yield and quality while minimizing resource waste.
The Importance of Nutrition in Hydroponic Systems
Unlike traditional soil-based farming, hydroponic systems rely entirely on nutrient solutions to deliver the necessary elements for plant growth. These nutrients must be provided in precise amounts to prevent deficiencies and toxicity. With aeroponic farming gaining popularity, ensuring a well-balanced nutrient mix becomes even more crucial as plants receive nutrients in a mist form rather than through water or soil.
Essential Nutrients in Hydroponic and Aeroponic Farming
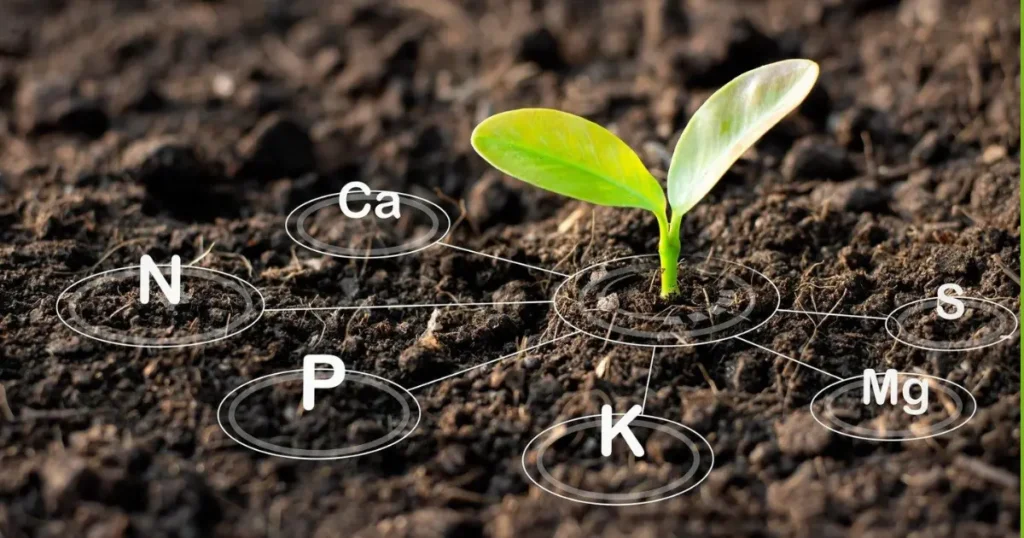
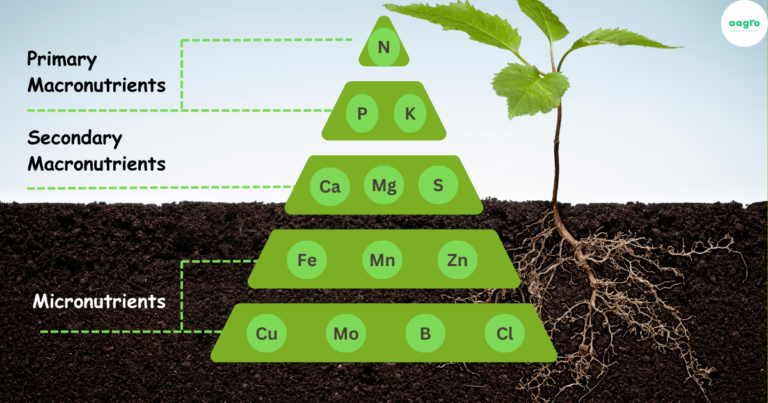
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the primary elements required for plant growth and are needed in large quantities. These include:
Nitrogen (N)
.
Essential for leafy growth, nitrogen supports chlorophyll production and overall plant metabolism. In aeroponic farming, nitrogen is supplied in nitrate or ammonium form for optimal absorption.
Phosphorus (P)
.
A key player in energy transfer, phosphorus is vital for root development, flowering, and fruit production. It is usually provided as phosphates in hydroponic solutions.
Potassium (K)
.
Enhancing disease resistance and water regulation, potassium supports enzyme functions and overall plant health.
Calcium (Ca)
.
Crucial for cell wall development, calcium prevents disorders such as blossom-end rot in tomatoes and peppers. Since aeroponic farming does not use soil, calcium must be meticulously maintained in nutrient solutions.
Magnesium (Mg)
.
The central component of chlorophyll, magnesium aids in photosynthesis and energy production.
Sulfur (S)
.
Essential for amino acid formation and protein synthesis, sulfur is often found in hydroponic nutrient formulations.
Micronutrients
Although needed in smaller quantities, micronutrients play a crucial role in plant health and growth. These include:
Iron (Fe)
.
Vital for enzyme functions and chlorophyll synthesis, iron deficiency can cause yellowing leaves.
Manganese (Mn)
.
Helps in photosynthesis and nitrogen assimilation.
Zinc (Zn)
.
Promotes enzyme activity and assists in growth regulation.
Copper (Cu)
.
Essential for reproductive growth and enzyme activation.
Boron (B)
.
Supports cell division and fruit/seed development.
Molybdenum (Mo)
.
Aids nitrogen fixation, allowing plants to efficiently use nitrogen-based nutrients.
How Aeroponic Farming Optimizes Nutrient Absorption
Aeroponic farming stands out as one of the most efficient methods of hydroponic agriculture. By delivering nutrients in a fine mist, aeroponic systems enhance absorption rates, ensuring plants receive precise amounts of essential minerals without excess waste. The advantages include:
Faster Growth Rates
.
Aeroponic farming accelerates nutrient uptake, leading to shorter growth cycles.
Reduced Water Usage
.
Compared to traditional hydroponic methods, aeroponics uses up to 95% less water while delivering the same, if not better, nutrient efficiency.
Lower Risk of Disease
.
Without standing water or soil, aeroponic farming reduces fungal and bacterial infections that often plague traditional farms.
Controlled Nutrient Delivery
.
The ability to fine-tune nutrient solutions ensures plants receive exactly what they need, when they need it.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies in Hydroponic and Aeroponic Systems
Nutrient imbalances can lead to deficiencies, negatively affecting plant health. Some common nutrient-related problems in hydroponic systems include:
Nitrogen Deficiency
.
Yellowing leaves and stunted growth.
Phosphorus Deficiency
.
Dark green or purplish foliage and poor root development.
Potassium Deficiency
.
Weak stems and scorched leaf edges.
Calcium Deficiency
.
Blossom-end rot and distorted leaf growth.
Iron Deficiency
.
Yellowing leaves with green veins (interveinal chlorosis).
Regular monitoring of nutrient levels and adjusting solutions accordingly can help prevent these issues in aeroponic farming setups.
Best Practices for Maintaining Optimal Nutrition in Hydroponic Systems
Use High-Quality Nutrients
.
Invest in hydroponic-specific nutrient formulations designed for aeroponic farming.
Monitor pH Levels
.
Maintain a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 to optimize nutrient absorption.
Adjust Nutrient Concentrations
.
Regularly test and adjust nutrient solutions to meet plant-specific requirements.
Ensure Proper Oxygenation
.
In aeroponic systems, keeping roots well-oxygenated enhances nutrient uptake.
Prevent Nutrient Lockout
.
Avoid excessive nutrient build-up by flushing systems periodically.
Use Automated Dosers
.
Automated nutrient dosing ensures consistent and accurate delivery, reducing human error.
-
Bacteria: The Remarkable Role of Microbes for Growing Plants in Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics: The Rookie Mistakes of Growing Plants
-
Chlorine: The Incredible Key to Thriving Hydroponic Plants
-
Molybdenum: Astonishing Importance for Hydroponic Plant Growth
-
Boron: The Astonishing Importance for Plants Growing in Hydroponics
-
Copper: A Powerful Element for Hydroponic Plant Growth
-
Zinc: The Powerful Secret to Hydroponic Plant Growth
-
Manganese: Essential role for Hydroponic Plant Growth
-
Iron: The Crucial Role of Iron in Hydroponic Plant Growth
-
Sulfur: The Vital Key to Thriving Hydroponic Plant Growth
-
Magnesium: The Crucial Role for Thriving Hydroponic Plants
-
Calcium: The Critical Importance for Thriving Hydroponic Plants
Conclusion
Hydroponic systems, particularly aeroponic farming, rely heavily on a well-balanced nutrient solution to support plant growth. Understanding the essential macronutrients and micronutrients, as well as maintaining proper nutrient management, ensures healthy plants and higher yields. As sustainable agriculture continues to evolve, aeroponic farming remains at the forefront, offering an efficient and resource-conscious method of growing crops. By mastering nutrient application, farmers and growers can maximize production while minimizing environmental impact.
Would you like to explore more about hydroponic nutrient formulations or specific plant-based nutrient requirements? Let us know in the comments!